Why study Enterprise Risk Management by IRM ?
IRM's Enterprise Risk Management is the ideal qualification (Level 1 to 5) for anyone looking for a solid foundation in the theory and practice of effective risk management across range of sectors and business departments. There’s never been a better time to get qualified in risk management, help organisations with the economic recovery post-Covid-19 and increase your earning potential and career prospects.
Learning Outcomes
-
Enhanced technical knowledge
-
Increased earning potential
-
Faster Employability
-
Career progression
-
Global Job Opportunities
-
Access Managerial Positions
Key Benefits
-
Online Learning
-
Equivalent to Degree Level
-
Multiple Choice Exams
-
5000+ exam centers to 360 exam centers in India
-
Online Webinars with Industry Experts
Qualification Architecture
Walk through the amazing journey of Enterprise Risk Management from Level 1 to Level 5
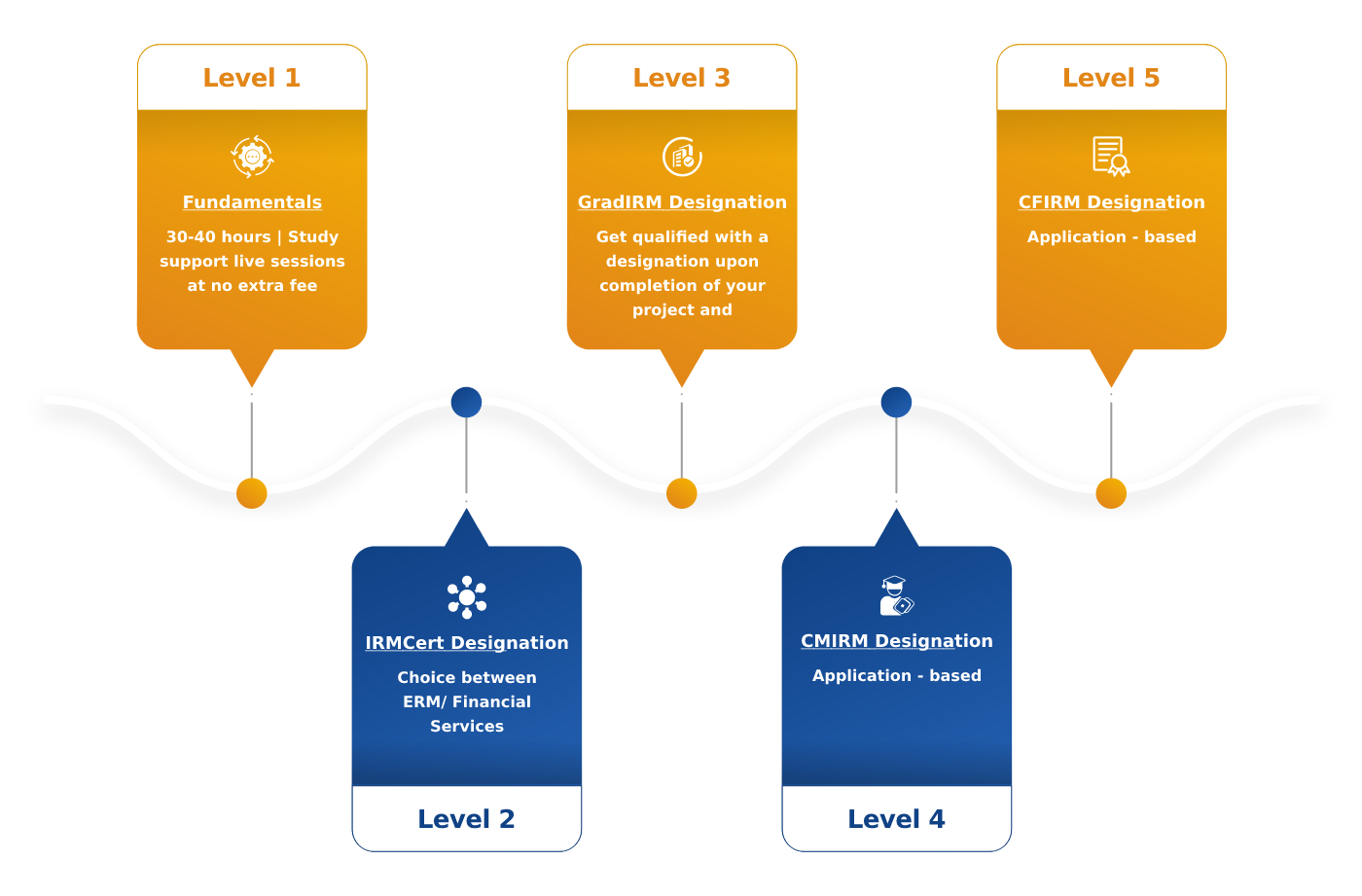
Qualification Overview

Level 1
Duration : 1.5 months (60 Hours)
Eligibility for Students:
Age : Minimum 18 years of ageEducation : At least XII grade
Work experience : No experience OR up to maximum 24 months’ experience
Eligibility for Professionals:
Age : Minimum 21 years of ageEducation : At least graduation
Work experience : Minimum 24 months’ full time work experience in any field/sector (except risk management)
- Understanding risk maturity
- Understanding the risks around us
- Global interconnected events
- Case studies on business failures
Introduction
- Learn how to define risk
- Understanding how risk management can be used to both maximise opportunities and minimise threat
- Understanding the principles and processes of risk management
- Establishing the attributes of effective risk management
What is Risk?
- Understanding the purpose and scope of risk management
- Establishing the relevant risk framework including roles and responsibilities and policies
- Develop an awareness of risk appetite
Context and Objectives
- Identification techniques
- Assessing risk and selecting appropriate actions and controls using key tools, such as risk registers, risk bow-ties and risk matrices.
- Practically applying risk assessment using case studies to identify and analyse
Risk Assessment
- Understanding risk treatment plans
- Recognising control effectiveness
- Awareness of business resilience
Risk Action
- Techniques to keep the risk management process alive
- Develop and appreciation of effective risk reporting
- Communicate risk to all levels and to external stakeholders
Communication and Reporting

Level 2
Duration : 6 - 9 months (400 Hours) (Choose any one)
Eligibility : IRM Level 1 qualified OR 2-3 years of experience in risk managementInternational certification in : Choose from elective option - Enterprise Risk Management or Financial Services Risk Management
Module 1:
Principles of Risk and Risk Management
- ERM - Unit 1: Concepts and definitions of risk and risk management
A general introduction to some basic risk management concepts. - ERM - Unit 2: Risk management standards
Explores the main features of key risk management standards, including the most generally accepted ISO 31000 standard (ISO, 2018), as well as some specialist risk management standards. - ERM - Unit 3: Enterprise Risk Management
An overview of ERM. Understand how it can be implemented, in what context and the role of objective setting. - ERM - Unit 4: Risk assessment 1 (introduction and identification)
Risk assessment is a key element of the process of ERM. This module introduces this wide-ranging subject following the ISO 31000 process. - ERM - Unit 5: Risk assessment 2 (analysis and evaluation)
This unit focuses on two elements, risk analysis and risk evaluation. Other professional standards are also examined. - ERM - Unit 6: Risk response and risk treatment
A conclusion of the module, completing the ERM process and considering risk treatment.
Module 2:
Practice of Risk Management
- ERM - Unit 1: The global business environment
The implications of the business and risk environment on organizations and appropriate responses. - ERM - Unit 2: Risk strategy and framework
The importance of a coherent risk framework, strategy and protocol, and the appropriate role of risk management documentation. - ERM - Unit 3: Risk culture, appetite and tolerance
How an organization's approach to risk management is significant, how to create effective risk profiles to manage this and what makes a great risk practitioner. - ERM - Unit 4: Risk and organizations
Key features of international corporate governance, how to manage regulatory bodies and various facets of risk management. - ERM - Unit 5: Risk assurance and reporting
Important features of an effective control environment and how auditing and other risk assurance techniques fit within the risk management framework. - ERM - Unit 6: Case studies in organizational risk management
Case studies that give important insights into how risk events occur, and the lessons that can be learned from them. Also covers the challenges of understanding emerging risks.
Module 1:
Principles of Risk and Risk Management in Financial Services
- RMF - Unit 1: The global business environment
The implications of the business and risk environment on organizations in financial services and appropriate responses. - RMF - Unit 2: Risk management standards
Explores the main features of key risk management standards, including the most generally accepted ISO 31000 standard (ISO, 2018), as well as Basel III and Solvency II. - Unit 3: Enterprise Risk Management
An overview of ERM. Understand how it can be implemented, in what context and the role of objective setting. - RMF - Unit 4: Risk assessment 1 (introduction and identification)
Introducing risk assessment, the importance of risk identification, some general risk assessment considerations and techniques that are used specifically in financial services. - ERM - Unit 5: Risk assessment 2 (analysis and evaluation)
This unit focuses on risk analysis, risk evaluation and the role of internal models in financial services. Focus on likelihood, impact and the positive side of risks. - ERM - Unit 6: Risk response and risk treatment
A conclusion of the module, completing the ERM process and considering risk treatment.
Module 2:
Practice of Risk Management in Financial Services
- ERM - Unit 1: The global business environment
The implications of the business and risk environment on organizations in financial services and appropriate responses. - ERM - Unit 2: Risk strategy and framework
The overall approach to risk management in financial services and how this can be structured to meet the needs of the organization. - ERM - Unit 3: Risk culture, appetite and tolerance
How an organization's approach to risk management is significant, how to create effective risk profiles to manage this and what makes a great risk practitioner. - ERM - Unit 4: Risk and organizations
Key features of international corporate governance, how to manage regulatory bodies and various facets of risk management including financial services. - ERM - Unit 5: Risk assurance and reporting
Important features of an effective control environment and how auditing and other risk assurance techniques fit within the risk management framework. - ERM - Unit 6: Case studies in organizational risk management
Case studies that give important insights into how risk events occur, and the lessons that can be learned from them. Also covering the challenges of understanding emerging risks.
Career Progress Levels
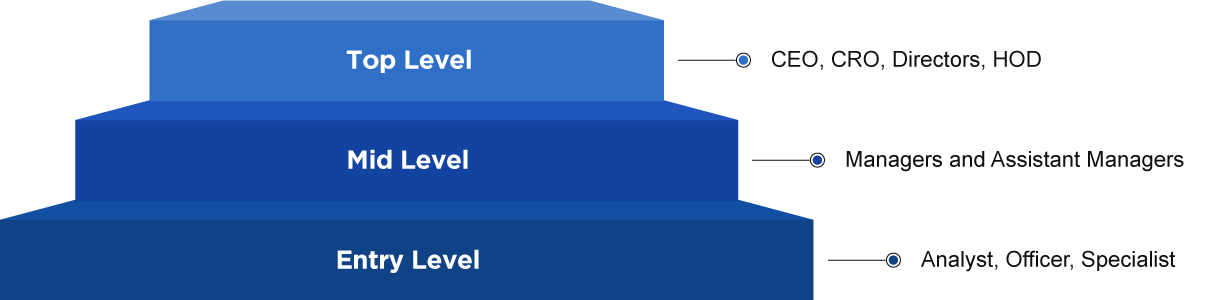

Why are Risk Managers Hired by Companies?
An organization that effectively and efficiently manages its risks and opportunities is more likely to achieve its business objectives at lower overall costs. Risk management is an inherent part of good management.
- Enhancing business performance.
- Improving risk decision making.
- Best risk management practice.
- Create a robust business plan.
- Risk-Ready for any unforeseen events.
Upcoming Level 1 Examination Dates
IRM’s examinations are online and computer-based. Module content will be assessed through the use of the learning outcomes.
2021
(Enrollment Closed)
2021
(Enrollment Closed)
2021
(Enrollment Closed)
2021
(Enrollment open. Last date to enroll 30th September 2021)
Try out our enterprise risk management quiz
Check out the interactive quiz to test your knowledge about ERM.
Start the QuizCareer Profiles
- Enterprise Risk Management
- Financial Risk Management
- IT Risk Management
- Insurance Management
- Employee Benefits Manager
- Claims Manager
- Business Continuity Manager
- Safety Manager
- Enterprise Risk Analyst
- Financial Risk Analyst
- Insurance Risk Analyst
- Claims Analyst
- Risk Management Specialist
- Risk Management (Internal Audit)
- Credit Risk Analyst
- Operational Risk Management
- Senior Risk Auditor
- Workers’ Compensation
- Insurance and Risk Management
- Chief Risk Officer
Frequently Asked Questions
Risk Management was traditionally studied with a focus on Financial Risk or Insurance Risk. While both those areas of risk are important, IRM's Qualifications cover Enterprise Risk Management and ERM is a much broader concept since it covers risks across the entity in all departments and all sectors, including supply chain, operations, human resources, marketing, branding & reputation, research & development, treasury, sales and much more. Additionally, financial risk management is a more quantitative subject, whereas ERM is more qualitative. Whether the candidate wants to pursue a career in risk or not, IRM's global qualifications are relevant for start-ups, family businesses and for all sectors in the industry including pharmaceuticals, financial services, FMCG, retail, manufacturing, technology and others.
IRM is a globally recognised, not-for-profit, professional education body, headquartered in the UK with presence in 143 countries. IRM is run by professional members across the world since 1986.
No, Enterprise risk management covers an organisation wide perspective which includes risk from procurement, supply chain, marketing, HR, reputation, technology, sales and many other areas. Whether you’re a marketing head or a business owner or a budding entrepreneur, IRM’s enterprise risk management qualifications help you build resilience and risk knowledge required in today’s uncertain world.
Because risk is inherent in everything we do, our students and members across the globe in 143 countries come from varied backgrounds - leadership, risk heads, family businesses, consulting and across sectors including health, insurance, energy, pharmaceuticals, financial services, etc.
IRM’s Qualifications (Level 1 to Level 5, DRM, SCRM) are valid for lifetime.
Level 1 and Level 2 can be pursued alongside graduation. It is highly recommended that candidates take the Level 3 Examination after completing their graduation.
- Big 4 consulting firms in risk management
- Risk based assurance in consulting and auditing firms
- Strategic risk management at consulting firms
- Credit rating agencies in risk management teams
- Risk and credit teams at banks/NBFCs
- Industry - FMCG, Pharma, Retail, Financial Services, Technology, Manufacturing, Agriculture, Steel - all listed, large companies have a risk management department as per requirement by SEBI/RBI/Companies Act 2013
- Start-ups, family-owned businesses, SMEs - new scope in a post crisis world as most businesses are setting up a risk and crisis team
